You are hereFigures & Facts
Figures & Facts
Rome. World leaders: food prices go higher - wheat might rise by 60%, vegetable oils by 80%
(quote)
Higher food prices may be here to stay as demand from developing countries and production costs rise, says an report by the UN's Food & Agriculture Organization (FAO) and the body for rich nations, the OECD. In its annual Outlook report, the FAO predicted beef and pork prices might be 20% higher by 2017, wheat could be up to 60% more expensive and the cost of vegetable oils might rise by 80%. World prices for wheat, maize and oilseed crops doubled between 2005 and 2007, and while the FAO expects these prices to fall, the decline may be slower than after previous spikes. As well as key factors such as weather, supply and demand and energy costs, speculators are also to blame for making commodity prices more volatile, the FAO says. It is also concerned about the increasing use of crops for biofuels. Looking ahead, climate change may also affect crop harvests, pushing up prices further.
But the hardest-hit by rising food costs will be the poorest people on the planet, where a large share of income is spent on food, the FAO warned. The FAO believes the commodity boom has forced some in the developing world to spend more than half their income on food, particularly those countries that have to import much of their food. But even then, its outlook may be too conservative, says BBC international development correspondent David Loyn, since predicting future oil prices is a near-impossible task. One key assumption made is that crude oil prices will peak at $104 a barrel by 2017 says our correspondent. But as he points out, the price is already well above that, and some reputable analysts are now predicting oil will go to $200 a barrel. And he added that while there may be a drop in food prices in coming years, "there is a sting in the tail. "Prices will level off at a far higher average level than seen before the crisis erupted," he said. "The long era of cheap food is over." read more »
US military suicides: 2,200 soldiers died within 2yrs of leaving service. 1 veteran dies by suicide per 80 minutes, 18 each day
(quote)
*Update Sep. 11, 2012*
Curbing Suicide Now a National Priority - Hoping to curb the escalating suicide rate in the United States, especially among military personnel and young Americans, health officials are spearheading a program that encompasses Facebook and other private companies.
"America loses approximately 100 Americans every 24 hours from suicide," said Pamela Hyde, administrator of the U.S. Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration, at a press conference Monday morning. Among people 18 to 24, suicide is now the third leading cause of death, officials said.
U.S. Surgeon General Dr. Regina Benjamin said, "It's time to turn our attention to prevention." The new strategy brings together government, the private sector, schools and communities to raise suicide awareness, increase prevention efforts and develop new treatments for those at risk, she said, speaking at the news conference.
In 2009, more than 37,000 Americans took their own lives, and "more than 500,000 Americans were depressed enough to have actually tried it," Hyde said. This is as critical a public health issue as good drinking water, safe food and infectious-disease prevention, Hyde said.
The military has been hit particularly hard. "Right now we are losing more of our soldiers to suicide than we are to combat," said Army Secretary John McHugh. Kathleen Sebelius, secretary of the Department of Health and Human Services, said that in July alone "the Army lost 38 soldiers to suicide - an all-time and month high."
*Update Feb. 25, 2012* read more »
50 ideas to save energy, save money, and get healthier and fit – all while on vacation
50 ideas to save energy, save money, and get healthier and fit – all while on vacation: from Inn-to-Inn Horseback Riding in Ireland, to New Zealand Multisport Adventure, to Everglades Multiday Kayaking Tour -
(quote)
All told, active travel accounted for an estimated $60 billion in vacation spending in 2007. "It used to be that adventure travel was very physical and risky, like climbing Mount McKinley," says Shannon Stowell, president of the Adventure Travel Trade Association and coauthor of Riding the Hulahula to the Arctic Ocean, a guide for adventure-hungry boomers.
The choices vary widely in terms of physical demands and comfort. At travel site iExplore.com, for example, trips considered "easy" involve nothing more than normal walking while sightseeing. A "moderate" rating might require three to five hours of physical activity daily. To go on a challenging trip, you must be fit enough to hike or bike for up to seven hours over steep or rugged terrain at elevations that sometimes exceed 10,000 feet. Typically, tour operators tailor activities to suit the group, offering more than one route to a destination, for example, and support vans to transport anybody who needs to take a break. Some offer deluxe lodging and meals to delight foodies; others put up tents at remote campsites and cook over the fire.
You won't fully enjoy even the easiest trips without some physical exertion, so if you haven't already, develop a workout routine well before your departure date. "Otherwise, better to hang out on the beach," warns Stowell.
Here's a sampling of options: read more »
Cellulosic Ethanol Plant Opens, Uses Waste Biomass to Make Biofuel
Original Source: Technology Review
(quote)
A biorefinery built to produce 1.4 million gallons of ethanol a year from cellulosic biomass will open tomorrow in Jennings, LA. Built by Verenium, based in Cambridge, MA, the plant will make ethanol from agricultural waste left over from processing sugarcane. It is the first demonstration-scale cellulosic ethanol plant in the United States and will be used to try out variations on the company's technology and is designed to run continuously. Verenium wants to demonstrate that it can create ethanol for $2 a gallon, which it hopes will make the fuel competitive with other types of ethanol and gasoline. Next year, the company plans to begin construction on commercial plants that will each produce about 20 to 30 million gallons of ethanol a year. Until now, technology for converting nonfood feedstocks into ethanol has been limited to the lab and to small-scale pilot plants that can produce thousands of gallons of ethanol a year. Since these don't operate continuously, they don't give an accurate idea of how much it will ultimately cost to produce cellulosic ethanol in a commercial-scale facility.
Almost all ethanol biofuel in the United States is currently made from corn kernels. But the need for cellulosic feedstocks of ethanol has been underscored recently as food prices worldwide have risen sharply, in part because of the use of corn as a source of biofuels. At the same time, the rising cost of corn and gas have begun to make cellulosic ethanol more commercially attractive, says Wallace Tyner, a professor of agricultural economics at Purdue University. A new Renewable Fuels Standard, part of an energy bill that became law late last year, mandates the use of 100 million gallons of cellulosic biofuels by 2010, and 16 billion by 2022.
So far, however, there are no commercial-scale cellulosic ethanol plants in operation in the United States, although a number of facilities are scheduled to start production in the next few years. The Department of Energy is currently funding more than a dozen companies that will be building demonstration- and commercial-scale plants. One of these, Range Fuels, based in Broomfield, CO, plans to open a commercial-scale plant next year. It will have the capacity to produce 20 million gallons of ethanol and methanol a year. Verenium will use a combination of acid pretreatments, enzymes, and two types of bacteria to make ethanol from the plant matter--called bagasse--that's left over from processing sugarcane to make sugar. It will also process what's called energy cane, a relative of sugarcane that's lower in sugar and higher in fiber. The high fiber content allows the plants to grow taller, increasing yield from a given plot of land.
The opening of the demonstration plant, and the current construction of a number of other demonstration- and commercial-scale cellulosic ethanol plants, marks a turning point for the industry, Riva says. The development of improved enzymes and fermentation organisms means that no further scientific breakthroughs are needed to make cellulosic ethanol commercially successful, he says. "There's been a tremendous amount of background work in science and technology development," he says. "We've learned so much about the process that the really important thing now is to start to deploy the technology at a commercial scale."
(unquote)

Japan Urges Limit on Cell Phone Use by Kids
(quote)
TOKYO (AFP) — A Japanese government panel called on parents and schools Monday to help limit the use of mobile phones by children to prevent them from accessing "harmful" information on websites. The advisory council on education made the proposal to Prime Minister Yasuo Fukuda as children become more prone to crimes involving dating websites and bullying on Internet school bulletin boards. The panel said it would urge "parents, schools and other people concerned to cooperate in preventing elementary and junior high school students from using mobile phones unless it is necessary." It called for limiting mobile phone use just to calls.
These measures are necessary to "protect children from harmful information and other negative influence involving the use of mobile phones" including "crimes and bullying," the report said. Press reports have linked some crimes by children to dating websites. "It is true that the use of mobile phones causes various problems," Fukuda told reporters. "I think the panel has made timely discussions on the problem." He added: "First of all, I wonder if there is any need for children to possess mobile phones."
While about a third of Japanese primary school students aged 7-12 use mobiles, by the time they get to high school that figure rises to 96 percent, according to a government survey last December. There are fears for students' safety as only about one percent of them have blocks on potentially harmful material, meaning they could reveal personal information, making them prey for fraudsters and pedophiles. But even on protected sites such as school bulletin boards, bullies are able to anonymously post comments without teacher oversight or intervention.
(unquote)
Images Courtesy of AFP and blog.pcnews.ro


Original Source: AFP
Euro, Franc, Krona to Benefit From Oil, U.S. dollar ranks bottom
Original Source: Bloomberg
(quote)
May 26 (Bloomberg) -- Currencies in Europe will benefit from record oil prices because of the region's energy efficiency, exports to oil-producing nations and vigilance against inflation, according to Barclays Capital. The euro, the British pound, the Swiss franc, the Swedish krona and the Norwegian krone should perform "relatively well" as oil prices rise, wrote David Woo, global head of foreign exchange strategy in London at the bank, the third-biggest currency trader. The U.S. dollar ranks bottom in terms of potential performance as energy prices climb, it said. "Europe is well positioned in the new paradigm, the U.S. is not," Woo wrote in a research note dated May 23.
The dollar slid as much as 8.9 percent to a record low against the euro this year as losses from the subprime mortgage collapse threatened to send the U.S. economy into a recession. At the same time, oil futures have soared to a record as a crude producers sought higher dollar prices to compensate for lower import revenues, according to Barclays Capital. This has created a "vicious circle'' where high energy prices increase the U.S. trade deficit and make other central banks reluctant to lower interest rates, leading to further dollar declines, Barclays Capital said. The euro bought $1.5757 at 5:23 p.m. in Tokyo, little changed from late in New York on May 23. It rose to $1.6019 on April 22, the highest since the common European currency's introduction in January 1999.
The U.S., Canadian, New Zealand and Australian score poorly in terms of their intensity of energy use because of their dispersed populations and focus on manufacturing or commodity industries, Barclays said. European economies are more densely populated, service-orientated and energy efficient, it said. Oil consumption accounts for less than 2 percent of nominal gross domestic product in Norway, Switzerland, the U.K. and Sweden in 2006, compared with more than 3.5 percent in the U.S. and Canada, the report showed. "The U.S. is the world's third-largest oil producer but because of the high energy intensity of its economy, its petroleum trade deficit is not much smaller than the eurozone, which produces no oil," Woo wrote. Japan and Switzerland may also suffer deteriorating trade balances as oil prices rise, the report said. Crude oil for July delivery rose by 96 cents to $133.15 a barrel in after-hours electronic trading on the New York Mercantile Exchange. It reached $135.09 on May 22, the highest since trading began in 1983.
(unquote)
Next month marks the tenth anniversary of the European Central Bank, guardian of the euro, which itself will turn ten thereafter.
Images courtesy of AP Photo/Haraz N. Ghanbari and AFP


Rising Acidity in World’s Ocean Waters 100 Years Earlier than Predicted
(quote)
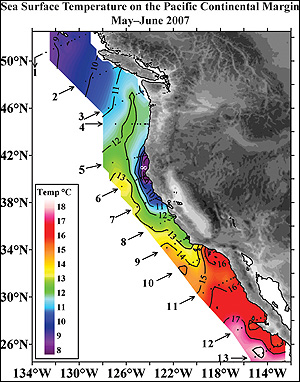
Climate models predicted it wouldn't happen until the end of the century. So Seattle researchers were stunned to discover that vast swaths of acidified sea water are already showing up along the Pacific Coast as carbon dioxide from power plants, cars and factories mixes into the ocean. In some places, including Northern California, the acidified water was as little as four miles from shore.
"What we found ... was truly astonishing," said oceanographer Richard Feely, of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Pacific Marine Environmental Laboratory in Seattle. "This means ocean acidification may be seriously impacting marine life on the continental shelf right now." The phenomenon is an aspect of global warming scientists are just beginning to understand.
Acidified ocean water can be fatal to some fish eggs and larvae. It also interferes with the formation of shells and skeletons, harming corals, clams, oysters, mussels and the tiny plankton that are the basis of the marine food web. "Their shells dissolve faster than they are able to rebuild them," said Debby Ianson, an oceanographer at Fisheries and Oceans Canada and a co-author of the study published today in the online journal Science Express.
Since the Industrial Revolution, when humans began pumping massive amounts of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, the oceans have absorbed 525 billion tons of the greenhouse gas, Feely estimates. That's about a third of the man-made emissions during that time. By reducing the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, the oceans have blunted the temperature rise due to global warming. But they've suffered for that service, with a more than 30 percent increase in acidity.
"This is another example where what's happening in the natural world seems to be happening much faster than what our climate models predict," said Carnegie Institution climate scientist Ken Caldeira, whose work suggested it would be nearly 100 years before acidified water was common along the West Coast. And there's worse to come, the scientists warn. The acidified water upwelling along the coast today was last exposed to the atmosphere about 50 years ago, when carbon-dioxide levels were much lower than they are now. That means the water that will rise from the depths over the coming decades will have absorbed more carbon dioxide, and will be even more acidic. "We've got 50 years' worth of water that's already left the station and is on our way to us," study co-author Hales said. "Each one of those years is going to be a little bit more corrosive."
(unquote)
Images courtesy of Dana Greeley & Simone Alin, PMEL, and Daily Mail

Original Source: Seattle Times